How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. Mastering drone operation requires understanding its components, pre-flight checks, basic and advanced flight maneuvers, camera controls, and importantly, safety and legal regulations. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We will cover everything from the fundamental mechanics of your drone – from propellers to flight controllers – to advanced techniques such as navigating windy conditions and capturing stunning aerial imagery. Safety is paramount, so we’ll also delve into crucial pre-flight checks, emergency procedures, and legal compliance, ensuring you fly safely and legally. By the end, you’ll be ready to embark on your drone piloting journey with confidence and skill.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various parts of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will cover the key components and introduce common terminology used in the drone community.
Drone Components and Their Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the interplay of several key components. Each part plays a vital role in its ability to fly and perform tasks. Here’s a breakdown:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust needed for lift and maneuverability. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into rotational motion. Brushless motors are commonly used for their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, this sophisticated piece of hardware manages all aspects of flight, including stability, orientation, and response to pilot inputs. It processes data from various sensors to maintain stable flight.
- Battery: Provides the power to run the motors and other electronic components. Battery capacity and type significantly impact flight time and performance.
- GPS Module (optional): Enables precise positioning and navigation, crucial for features like autonomous flight and Return-to-Home (RTH) functionality.
- Gimbal (optional): A stabilizing mount for the camera, ensuring smooth and steady footage even during flight maneuvers.
- Camera (optional): Captures photos and videos, offering various resolutions and features depending on the drone model.
- Radio Transmitter/Controller: Allows the pilot to control the drone’s movements and functions wirelessly.
Glossary of Common Drone Terminology, How to operate a drone
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terminology will greatly enhance your understanding and communication within the drone community.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating this process requires careful study and practice, and a great resource for learning is available at how to operate a drone , which offers comprehensive guidance. This website provides valuable insights into safe and effective drone piloting techniques, ensuring you’re well-prepared for your next flight.
- Altitude Hold: A flight mode that maintains a constant altitude.
- Gimbal Lock: A situation where the gimbal loses its ability to move freely in one or more axes.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): A feature that automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point.
- Throttle: Controls the vertical speed of the drone.
- Yaw: Rotation of the drone around its vertical axis.
- Pitch: Movement of the drone up or down around its longitudinal axis.
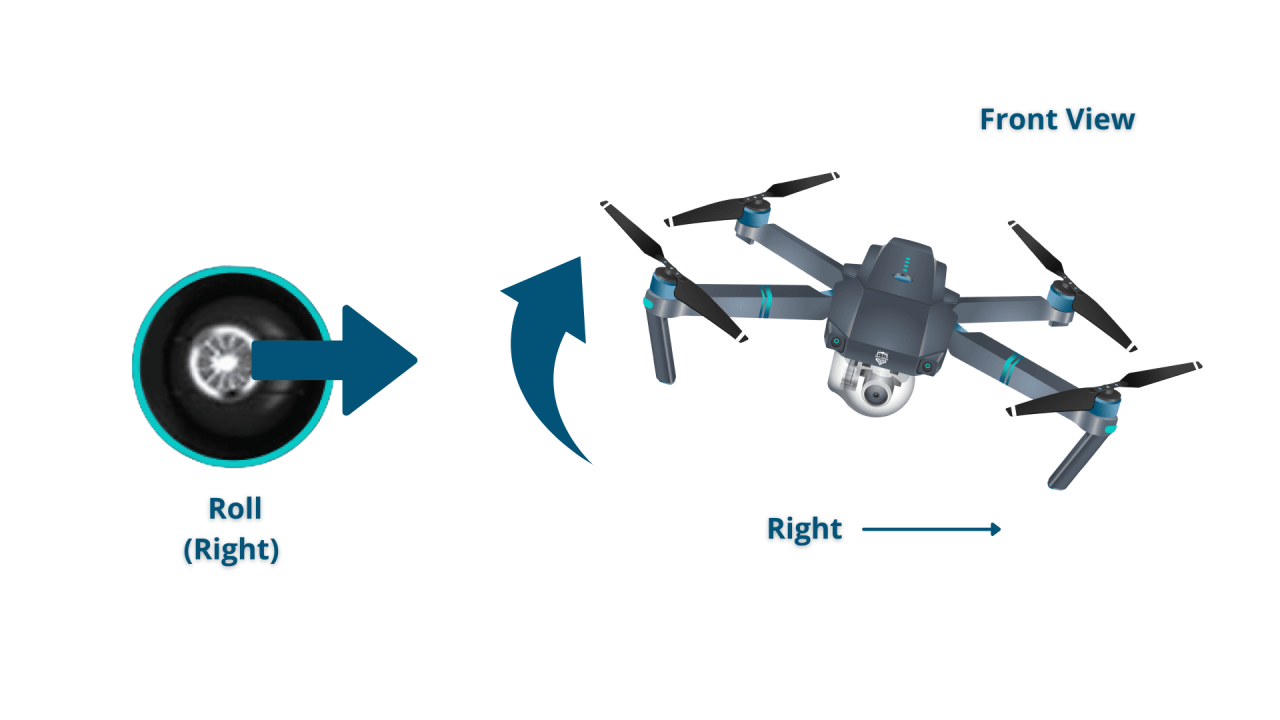
- Roll: Movement of the drone left or right around its lateral axis.
- LiPo Battery: Lithium Polymer battery, a common type of rechargeable battery used in drones.
Drone Battery Comparison
Different drone batteries offer varying performance characteristics. Choosing the right battery is essential for optimal flight time and safety.
| Capacity (mAh) | Voltage (V) | Flight Time (minutes) | Weight (grams) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1500 | 11.1 | 20-25 | 200 |
| 2200 | 14.8 | 30-35 | 300 |
| 3000 | 14.8 | 40-45 | 400 |
| 4500 | 22.2 | 50-60 | 600 |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is paramount for ensuring a safe and successful flight. Overlooking even minor details can lead to accidents or malfunctions.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously follow this checklist:
- Inspect the drone for any visible damage or loose parts.
- Check the propeller tightness and ensure they are securely fastened.
- Verify the battery level and ensure it’s fully charged.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) if necessary.
- Check the GPS signal strength (if applicable).
- Review the weather conditions and avoid flying in strong winds or rain.
- Ensure you have sufficient space for takeoff and landing.
- Confirm that you are in a legally permitted area to fly.
Importance of Propeller Tightness and Battery Levels
Loose propellers can cause vibrations and instability during flight, potentially leading to a crash. Insufficient battery charge can result in a sudden power loss mid-flight, causing an uncontrolled descent.
Pre-Flight Inspection Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight process can aid in efficient and thorough inspections.
The flowchart would begin with “Power On Drone and Controller”, followed by a decision diamond: “Drone and Controller Power On?”. A “Yes” branch would lead to a series of rectangular boxes representing the checklist items (visual inspection, propeller check, battery check, GPS check, weather check, location check). A “No” branch would loop back to the initial power-on step. After completing the checklist, a final rectangular box would indicate “Proceed to Takeoff” while a “No” response to any checklist item would lead to a separate box for troubleshooting and repair.
Taking Off and Landing
Proper takeoff and landing procedures are critical for maintaining drone safety and preventing damage. This section Artikels best practices for various conditions.
Safe Takeoff Procedures
A smooth and controlled takeoff involves gradually increasing the throttle, monitoring the drone’s stability, and making any necessary adjustments. Always ensure sufficient space and a clear flight path.
Smooth and Controlled Landings
Landing techniques should prioritize a gentle descent and stable positioning. In windy conditions, adjust for wind drift by compensating with the control sticks, and in confined spaces, make sure you have enough room to maneuver safely and execute a precise landing.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques Comparison
Assisted takeoff leverages features like GPS and altitude hold to simplify the process, while manual takeoff requires more precise control from the pilot. Assisted landing provides automatic descent and landing assistance, while manual landing necessitates careful throttle control and adjustments for a smooth touchdown.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the functions of the control sticks and performing basic maneuvers are fundamental skills for every drone pilot. This section provides a step-by-step guide to achieving stable hovering.
Functions of Control Sticks
The control sticks typically govern four axes of movement: Throttle (vertical movement), Pitch (forward/backward), Roll (left/right), and Yaw (rotation). Understanding the relationship between stick movements and drone response is key to precise control.
Basic Maneuvers
Basic maneuvers include hovering, moving forward/backward/sideways, and turning. These are achieved by carefully manipulating the control sticks, learning to maintain balance, and reacting to any drift.
Achieving Stable Hovering
Stable hovering at different altitudes involves fine-tuning the throttle and making small adjustments to counteract any wind or drift. Practice is crucial to master this fundamental skill.
- Begin by finding a level, open space.
- Slowly increase the throttle until the drone lifts off.
- Use small, precise movements of the control sticks to maintain a stable position.
- Gradually adjust the throttle to reach the desired altitude.
- Practice maintaining a stable hover for extended periods.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Flying in challenging conditions requires advanced skills and strategies. This section addresses flying in windy conditions and navigating obstacles.
Challenges of Flying in Windy Conditions
Wind can significantly impact drone stability and control. Strong gusts can push the drone off course, making precise maneuvers difficult. Solutions include adjusting flight parameters and utilizing features like wind compensation (if available).
Navigating Obstacles and Maintaining Safe Distances
Safe navigation involves careful planning, precise control, and maintaining awareness of the surrounding environment. Always maintain a safe distance from obstacles to avoid collisions.
Wind’s Effect on Drone Flight and Compensation
Wind affects drone flight primarily by exerting force on the drone’s body and propellers. This force can cause drift and instability. To compensate, the pilot must anticipate the wind’s direction and strength and make appropriate adjustments to the control sticks, applying counteracting forces to maintain stability and position. For example, if a headwind is present, the pilot needs to increase throttle to maintain altitude and counteract the force pushing the drone backward.
Similarly, crosswinds require adjustments to the roll and yaw controls to maintain the desired flight path. The stronger the wind, the more significant the adjustments needed to maintain stability and control.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is essential for capturing high-quality photos and videos. This section explains camera settings and framing techniques.
Drone Camera Settings
Typical drone camera settings include ISO (light sensitivity), shutter speed (exposure time), and aperture (lens opening). Adjusting these settings allows for control over image brightness, sharpness, and depth of field.
Framing Shots and Achieving Desired Compositions
Effective framing involves carefully positioning the subject within the frame to create visually appealing compositions. Consider rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional guidelines to enhance your images.
Camera Mode Comparison
Different camera modes offer various functionalities for different shooting styles.
| Mode | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photo | Captures still images. | High resolution, detailed images. | Limited dynamic range. |
| Video | Records moving images. | Captures action and movement. | Requires more storage space. |
| Timelapse | Creates a sequence of images over time. | Shows changes over time. | Requires longer shooting time. |
Battery Management and Safety: How To Operate A Drone
Proper battery management is crucial for extending battery lifespan and preventing safety hazards. This section covers charging, storage, and identifying signs of battery failure.
Proper Battery Charging and Storage
Always use the recommended charger and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for charging and storage. Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries, and store them in a cool, dry place.
Safety Precautions to Prevent Battery Overheating or Damage
Never leave charging batteries unattended. Avoid exposing batteries to extreme temperatures or direct sunlight. Inspect batteries regularly for any signs of damage.
Signs of a Failing Battery and Procedures to Follow
Signs of a failing battery include reduced flight time, unusual swelling, or leaking. If you observe any of these signs, immediately remove the battery from the drone and replace it with a new one. Dispose of damaged batteries properly.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic maneuvers. Learning the fundamentals is crucial before attempting complex flights; for a comprehensive guide on this, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. This will help you gain confidence and ensure safe and responsible drone operation, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable experience.
Emergency Procedures and Troubleshooting

Knowing how to handle emergencies and troubleshoot common problems is essential for safe drone operation. This section covers common malfunctions and emergency procedures.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Solutions
Common malfunctions include loss of signal, low battery, and motor failures. Solutions vary depending on the specific issue and may involve troubleshooting steps, software updates, or contacting support.
Handling Unexpected Situations
Procedures for handling unexpected situations like loss of control or low battery include activating the Return-to-Home (RTH) function (if available), attempting to regain control manually, and preparing for an emergency landing. Prioritize safety and attempt to minimize damage.
Emergency Contacts and Resources
Maintain a list of emergency contacts, including local authorities and drone support services. Familiarize yourself with online resources and forums that can provide assistance in case of emergencies.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to local drone regulations and airspace restrictions is crucial to avoid legal consequences. This section highlights the importance of compliance and potential consequences of violations.
Importance of Adhering to Local Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location and are designed to ensure safe and responsible drone operation. Failing to comply with these regulations can result in fines, legal action, or even criminal charges.
Situations Where Drone Operation Might Be Restricted
Drone operation might be restricted near airports, military bases, critical infrastructure, and during emergencies. Always check local regulations before flying.
Potential Consequences of Violating Drone Laws
Consequences of violating drone laws can include fines, license suspension or revocation, imprisonment, and damage to reputation.
Drone Maintenance and Care
Regular maintenance is vital for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of your drone. This section details a routine maintenance schedule and storage tips.
Routine Maintenance Schedule

A routine maintenance schedule should include regular inspections for damage, cleaning the drone after each flight, and lubricating moving parts as needed. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for specific maintenance tasks.
Importance of Cleaning and Inspecting the Drone
Cleaning and inspecting the drone after each flight removes dirt, debris, and potential damage, preventing further issues. Regular inspections can identify minor problems before they escalate.
Proper Storage When Not in Use
Store the drone in a cool, dry, and safe place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Keep the battery separate and properly stored to prevent damage or accidental discharge.
Successfully operating a drone involves a blend of technical understanding and responsible practice. From mastering basic flight controls to navigating complex situations, this guide has provided a framework for safe and efficient drone operation. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to honing your skills and expanding your capabilities. Always prioritize safety, respect regulations, and enjoy the thrill of flight responsibly.
Answers to Common Questions
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with intuitive controls and robust safety features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration should be performed before each flight, especially if you’re in a new location or near magnetic interference.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If the RTH fails, visually locate the drone and attempt to regain control. If unsuccessful, contact local authorities.
How do I ensure my drone footage is high quality?
Experiment with camera settings (ISO, shutter speed, aperture) to optimize for lighting conditions. Maintain a steady flight for smooth footage, and use proper framing techniques.
